Introduction
Game Theory
所有的智能体(agent)在同一个环境中,且都是自私理性(self-interested)的,博弈论研究这些智能体的行为。
这门课需要回答的问题:
- What to expect? 即 game 的最终状态,比如生态系统中生物最后的稳态分布。
- How good is it? 即最终的 game 的状态是否是好的状态。
- Can it be controlled? 即我们能否控制这个 game 使之达到一个好的状态。

3 Board Goals
Games and Equilibria
Understand outcomes arising from interaction of intelligent and self-interested agents.
需要知道:
- 是否存在均衡(equilibria)?
- 均衡是否唯一?
- 如何得到均衡?
Prisoner’s Dilemma

无论另一个人选什么,选择 C(confess) 对于自己来说结果总是更优的,因此两者都 confess 是唯一的均衡(equilibria)状态。但是对于两个囚徒而言,这个结果并不是最优的。
Static Games with Complete Information
- Model for strategic games: matrix games (Prisoner’s Dilemma) and continuous games (Cournot Game)
- Solution concepts: equilibrium hierarchy (几个 equilibrium 是从强到弱的关系)
- Dominant and Dominated Strategies
- Pure Nash Equilibrium (NE) and Mixed Nash Equilibrium
- Correlated Equilibrium
- Existence of NE: a fixed point of best-response correspondences.
- For finite games, Nash’s Theorem shows the existence of a mixed NE using fixed-point theorems.
- For continuous games, show the existence of pure NE under convexity assumption.
- For general continuous games, Glicksberg’s Theorem shows the existence of mixed NE.
- For discontinous games, existence of a mixed equilibrium established under some assumptions.
- Uniqueness of NE using “strict diagonal concavity”
没太搞懂
Price of Anarchy
Analyze quality of the outcome arising from strategic interaction, i.e. OPT vs NE.
即分析的是在博弈论中,每个个体的自私性对于整个系统总的结果的影响。
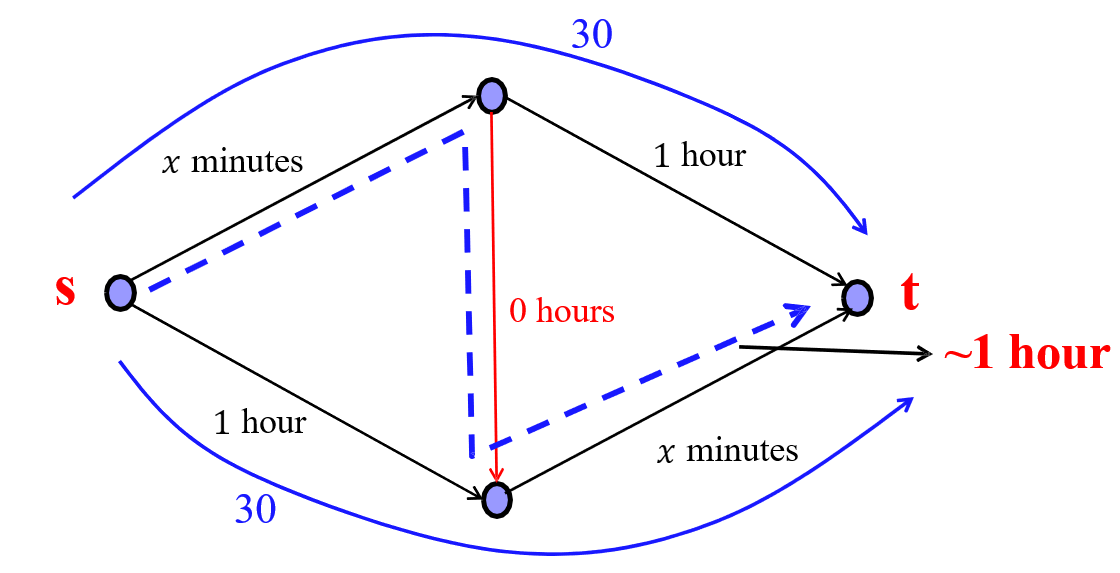
Braess’ Paradox

假设总共有 个人需要从起点 到终点 。对于图上标的两个 minutes 的路径,我们假设 ,其中 为走在这条路上的人数。那么每个人在追求自己时间最小化的情况下,两条路最终都会有 个人,所有人的总时间都是 分钟。
但是如果中间又新修了一条路
会发现所有人都会走 minutes 的那条路,导致 。那么所有人从 到 的时间变成了 分钟,结果反而更差了,这是作为 game 的结果。而在新的情况下,这个系统整体的最优解依然是像原来一样,时间应当为 分钟,这是作为 optimization 的结果。
于是我们可以得到新的情况的 Price of Anarchy (PoA) 为
PoA 就是用来衡量 game 的结果(outcome)的质量(quality),希望越小越好。
Mechanism Design
Designing rules to ensure “good” outcome under strategic interaction among selfish agents.
即如何设计 game 的规则(rule),使得最后的结果是好的,即让 PoA 更小。
More on Game Theory
Optimization Theory:
- Maximize
- Subject to
假设最后的解为 ,这就是一个 optimal 的解。
Game Theory:
- 共有 个 agent,每个 agent 选择一个 使得自己的 utility 最大。其中 也可以写成
在多个 agent 的共同作用下,也可以得到一个解,或者说是一个 equilibrium,记为 。
Example: Resource Allocation
资源有限,需要竞争。假设总共的资源为 ,有 个 agent 来竞争,并且这三个 agent 的 utility 分别为:
Optimization Problem:
可以解得最优情况为 ,总的 utility 约为 。
Game Problem:
系统不知道每个 agent 实际的 utility。每个 agent 为了最大化自己的 utility,都 report (假设这个就是最大值)。那么最终做出的分配就为 ,导致实际的总 utility 约为
strategy